先参照 IntelliJ IDEA 2016.1建立Strut2工程并使用Tomcat调试建立新的工程,一步一步操作,包括最后引用Spring框架部分。
经过上面的操作,Spring-WebSocket的包应该已经被默认引入了,如下图所示:
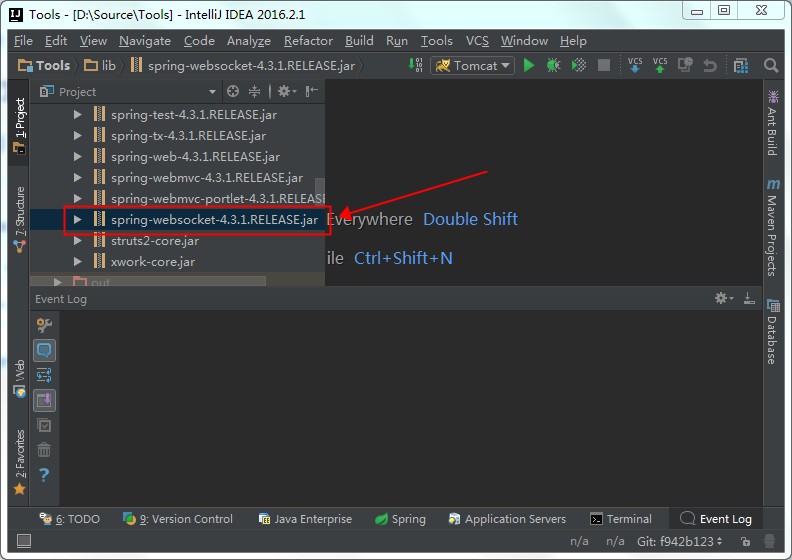
这就意味着我们已经不需要再进行过多的额外配置了。
接下来,我们在src->Tools下面新建一个WebSocket的目录,里面创建三个Java文件。如下图:
每个文件中的代码如下:
SystemWebSocketHandler.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 |
package Tools.WebSocket; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Date; import org.springframework.web.socket.CloseStatus; import org.springframework.web.socket.TextMessage; import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketMessage; import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketSession; import org.springframework.web.socket.handler.TextWebSocketHandler; public class SystemWebSocketHandler extends TextWebSocketHandler { private static final ArrayList<WebSocketSession> users = new ArrayList<>(); @Override public void afterConnectionEstablished(WebSocketSession session) throws Exception { System.out.println("ConnectionEstablished"); users.add(session); session.sendMessage(new TextMessage("connect")); session.sendMessage(new TextMessage("new_msg")); } @Override public void handleMessage(WebSocketSession session, WebSocketMessage<?> message) throws Exception { System.out.println("handleMessage" + message.toString()); session.sendMessage(new TextMessage(new Date() + "")); } @Override public void handleTransportError(WebSocketSession session, Throwable exception) throws Exception { if(session.isOpen()){ session.close(); } users.remove(session); } @Override public void afterConnectionClosed(WebSocketSession session, CloseStatus closeStatus) throws Exception { users.remove(session); } @Override public boolean supportsPartialMessages() { return false; } /** * 给所有在线用户发送消息 * * @param message */ public void sendMessageToUsers(TextMessage message) { for (WebSocketSession user : users) { try { if (user.isOpen()) { user.sendMessage(message); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } |
WebSocketConfig.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
package Tools.WebSocket; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketHandler; import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.EnableWebSocket; import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketConfigurer; import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketHandlerRegistry; @Configuration @EnableWebMvc @EnableWebSocket public class WebSocketConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter implements WebSocketConfigurer { @Override public void registerWebSocketHandlers(WebSocketHandlerRegistry registry) { registry.addHandler(systemWebSocketHandler(), "/webSocketServer").addInterceptors(new WebSocketHandshakeInterceptor()); } @Bean public WebSocketHandler systemWebSocketHandler() { return new SystemWebSocketHandler(); } } |
WebSocketHandshakeInterceptor.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
package Tools.WebSocket; import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpRequest; import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpResponse; import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketHandler; import org.springframework.web.socket.server.HandshakeInterceptor; import java.util.Map; public class WebSocketHandshakeInterceptor implements HandshakeInterceptor { @Override public boolean beforeHandshake(ServerHttpRequest serverHttpRequest, ServerHttpResponse serverHttpResponse, WebSocketHandler webSocketHandler, Map<String, Object> map) throws Exception { System.out.println("beforeHandshake"); return true; } @Override public void afterHandshake(ServerHttpRequest serverHttpRequest, ServerHttpResponse serverHttpResponse, WebSocketHandler webSocketHandler, Exception e) { System.out.println("afterHandshake"); } } |
由于我们使用了Struts2导致我们的网络请求优先被Struts2的拦截器拦截,而Struts2又处理不了websocket请求,结果直接返回了404错误。因此我们需要替换掉默认的在web.xml中定义的Struts2的拦截器,要求Struts2不处理websocket请求。
我们在src->Tools下面新建一个Filter的目录,下面创建一个名为StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilterEx.java的源代码文件,如下图:
具体的代码如下:
StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilterEx.java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
package Tools.Filter; import org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import java.io.IOException; public class StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilterEx extends StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter { @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp, FilterChain filter) throws IOException, ServletException { String requestURI = ((HttpServletRequest) req).getRequestURI(); if(requestURI != null && (requestURI.contains("/webSocketServer")) || requestURI.startsWith("ws://") || requestURI.contains("/mspjapi")) filter.doFilter(req, resp); else super.doFilter(req, resp, filter); } } |
这时候的代码是无法编译通过的,原因是依赖的javax的Jar包不存在。此时,我们需要手工引入javax.servlet:javax.servlet-api:3.1.0这个Jar包。如下图:
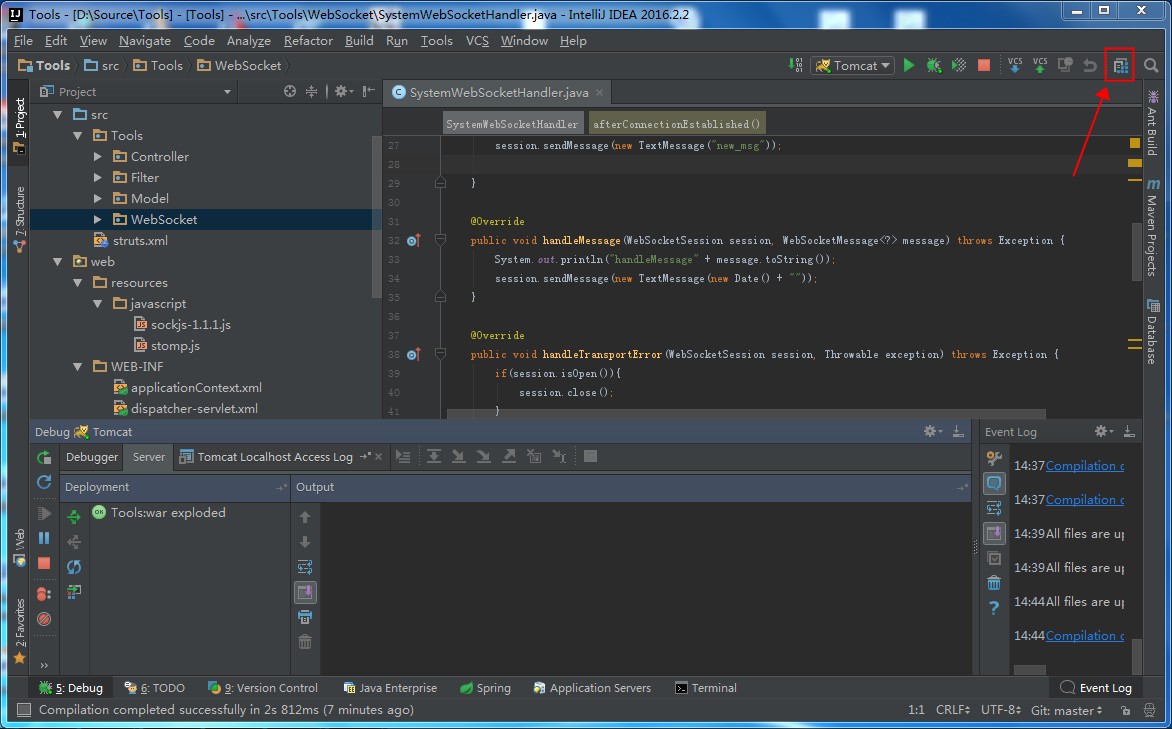
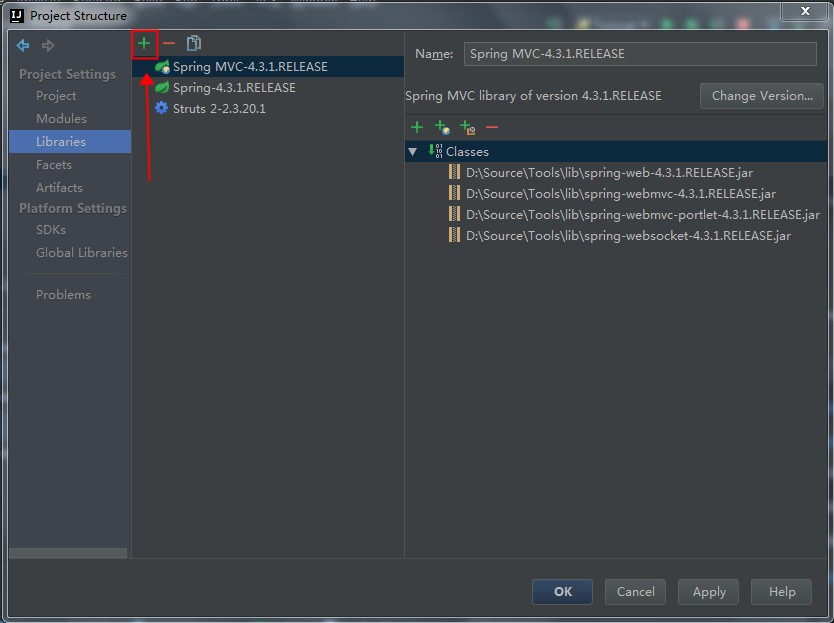
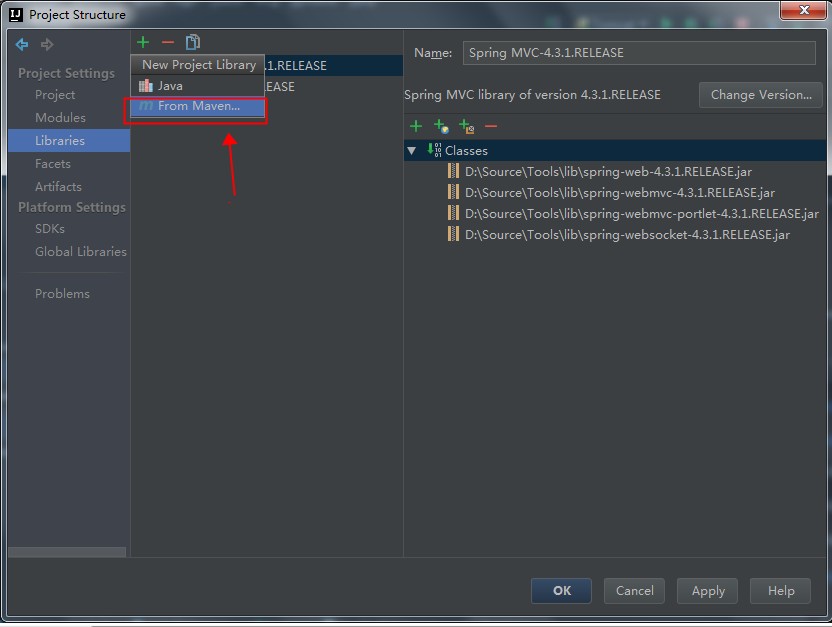
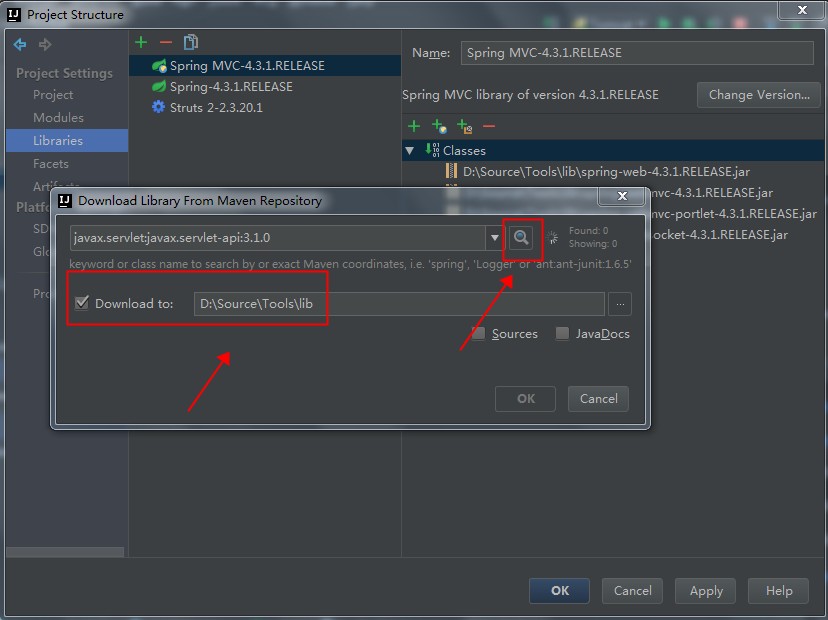
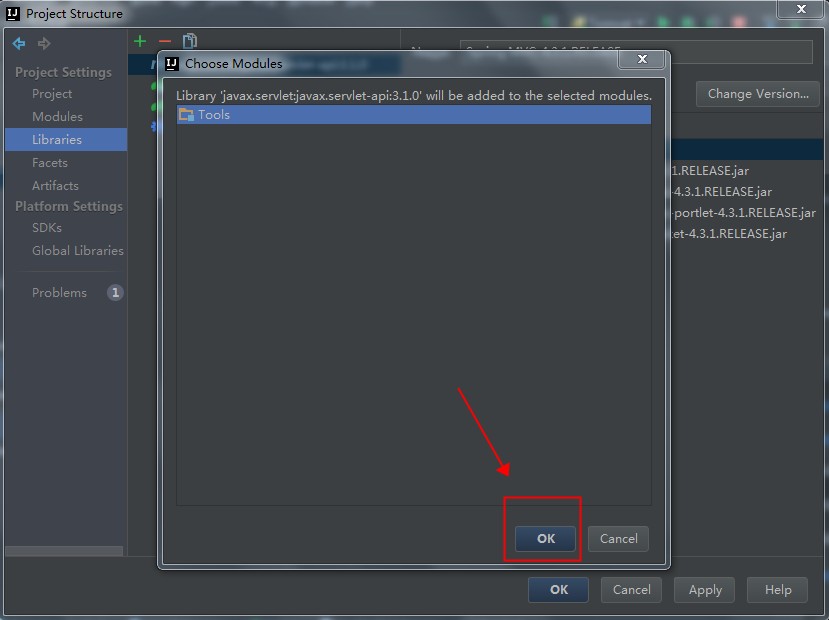
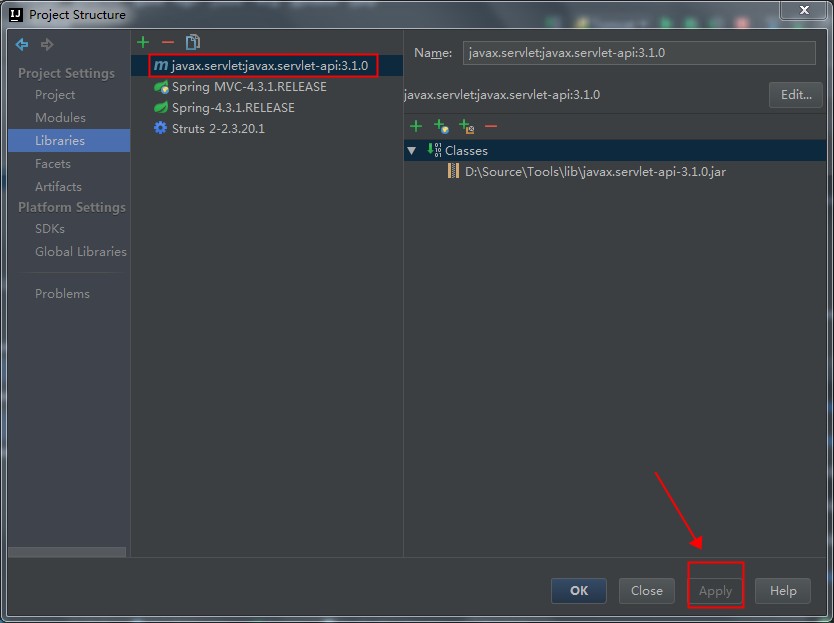
还要注意,刚刚添加进入的javax.servlet:javax.servlet-api:3.1.0这个Jar包,我们只在编译期间使用,在运行时候,使用Tomcat自己实现的那个同名Jar包。也就是这个包是个Provided,而不是Compile关系,具体如下图:
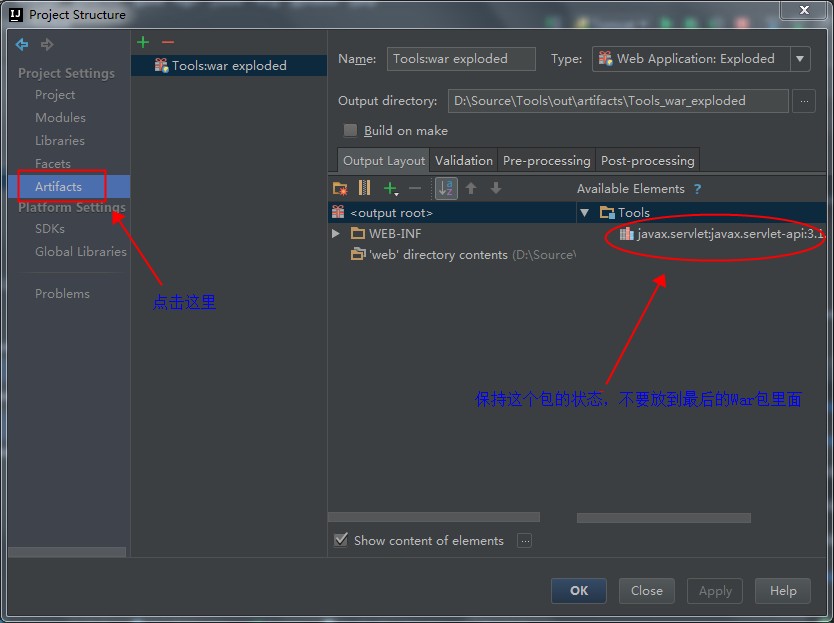
接下来,修改web.xml指定Struts2的拦截器为我们定义的拦截器
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
<filter> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> |
修改为
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
<filter> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <filter-class>Tools.Filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilterEx</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> |
经过上面的修改后,依旧是没办法进行网络访问的,原因是web.xml中的Spring拦截器并没有拦截WebSocket的数据请求。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
<servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> <async-supported>true</async-supported> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.form</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> |
修改为
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
<servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> <async-supported>true</async-supported> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.form</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/webSocketServer/*</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> |
注意增加的
|
1 |
<async-supported>true</async-supported> |
下一步,配置Spring的配置文件web->WEB-INF->dispatcher-servlet.xml增加配置信息类的扫描目录包含我们刚刚创建的src->Tools->WebSocket的目录(缺少这一步会导致我们通过注解实现的配置信息类没有被自动加载,导致无法访问),修改后的内容如下:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- Scan for spring annotated components --> <context:component-scan base-package="Tools.WebSocket"/> </beans> |
最后,调用的页面的代码
WebSocket.jsp
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 |
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>WebSocket</title> <style type="text/css"> #console-container { margin-left: 15px; margin-right: 15px; padding: 5px; width: 95%; } #console { border: 1px solid #CCCCCC; border-right-color: #999999; border-bottom-color: #999999; height: 300px; overflow-y: scroll; padding: 5px; width: 100%; } #console p { padding: 0; margin: 0; } </style> <script type="text/javascript"> var url = 'ws://' + window.location.host + '/webSocketServer'; var ws = new WebSocket(url); ws.onopen = function () { log('Info: connection opened.'); }; ws.onmessage = function (event) { log('Received: ' + event.data); }; ws.onclose = function (event) { log('Info: connection closed.'); log(event); }; function log(message) { var console = document.getElementById('console'); var p = document.createElement('p'); p.style.wordWrap = 'break-word'; p.appendChild(document.createTextNode(message)); console.appendChild(p); while (console.childNodes.length > 1000) { console.removeChild(console.firstChild); } console.scrollTop = console.scrollHeight; } </script> </head> <body> <div> <div id="console-container"> <div id="console"></div> </div> </div> </body> </html> |
最后的客户端显示效果如下图所示:
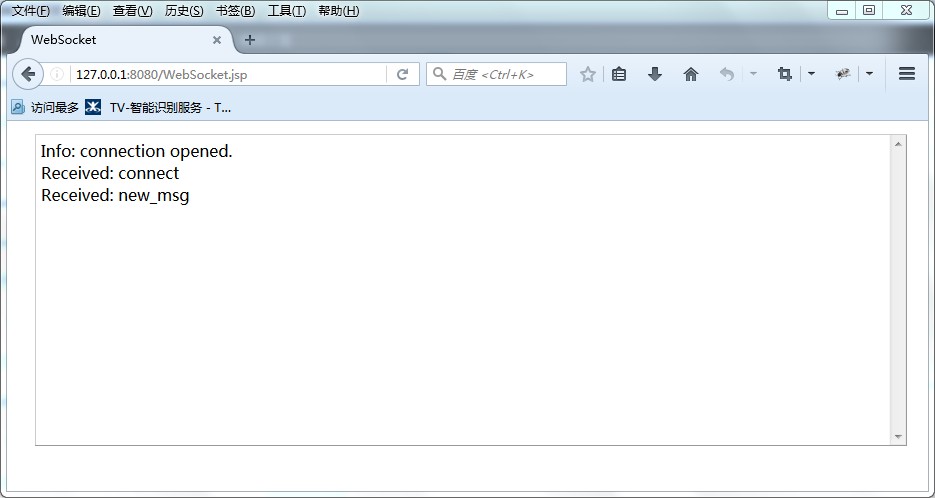
注意:如此创建的WebSocket是会在两三分钟后主动断开连接的,原因在于WebSocket需要周期性的发送心跳报文来维持连接。后续我们会尝试使用sockjs来实现自动发送心跳的逻辑。
具体的sockjs的接入方法,参考IntelliJ IDEA 2016.2使用Spring 4.3.1.RELEASE,sockjs-1.1.1,stomp-1.2搭建基于Tomcat-7.0.68的WebSocket应用