iMaker 3D打印机,已经在角落里面落灰许久了,本质上是一台 Ultimaker v1.5.7硬件的机器,因此使用 Ultimaker 的软件跟固件都是没有问题的。貌似这家公司现在已经快不行了的样子。 官网都已经打不开了。继续阅读iMaker 3D打印机Marlin固件编译以及故障排除
iMaker 3D打印机,已经在角落里面落灰许久了,本质上是一台 Ultimaker v1.5.7硬件的机器,因此使用 Ultimaker 的软件跟固件都是没有问题的。貌似这家公司现在已经快不行了的样子。 官网都已经打不开了。群晖 DSM 6.2 系统上执行 zgrep 命令的时候提示找不到命令,其他平台系统(ARM ),需要手工编译安装ZUtils,来提供。但是如果是 X86 系统的话(比如 DS718+ ),可以直接使用交叉编译环境里的工具,直接拷贝到系统即可。
首先参考 搭建群晖交叉编译环境(DS718+/ubuntu 16.04.6/DSM 6.2.1-23824 Update 6) 搭建群晖 DSM 6.2 的编译环境。
DS718+ 执行如下:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
$ cd ~/toolkit//build_env/ds.x64-6.2/ $ scp -r ./bin/zgrep username@10.10.10.111:~/ $ ssh 10.10.10.111 -l username $ sudo mv ~/zgrep /usr/local/bin/ |
需要编译的(ARM 芯片版本),执行如下命令编译:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
$ cd ~/toolkit/pkgscripts-ng # 下载 ZUtils 1.8 $ sudo wget http://deb.debian.org/debian/pool/main/z/zutils/zutils_1.8.orig.tar.xz -O ../build_env/ds.x64-6.2/root/zutils_1.8.orig.tar.xz # 也可以本站下载 sudo wget https://www.mobibrw.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/zutils_1.8.orig_.tar.xz -O ../build_env/ds.x64-6.2/root/zutils_1.8.orig.tar.xz $ sudo chroot ../build_env/ds.x64-6.2/ $ cd root $ export PREFIX="/root/build_libs" $ export HOST="x86_64-linux-gnu" $ mkdir -p $PREFIX # 编译 ZUtils 1.8 $ tar xvf zutils_1.8.orig.tar.xz $ cd zutils-1.8/ $ PKG_CONFIG_PATH=$PREFIX/lib/pkgconfig/ \ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$PREFIX/lib/ \ ./configure \ --prefix=$PREFIX $ make clean $ make $ make install |
对于编译好的程序,复杂的可以自己制作安装包,简单的可以直接通过SSH推送到设备的/usr/local/bin目录下即可。
比如本次编译结果:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# 暂时只需要zgrep,因此只安装 zgrep $ scp -r $PREFIX/bin/zgrep username@10.10.10.111:~/ $ ssh 10.10.10.111 -l username $ sudo mv ~/zgrep /usr/local/bin/ |
最近 Debian Wheezy/Jessie 源被官方归档了,使得许多来不及更新系统的服务器没源可用,http://archive.debian.org 访问速度太慢, 不得以自己写个脚本同步 Wheezy/Jessie 源。
Debian 官方推荐使用 debmirror 同步源,但是在群晖等设备上不方便使用,因此还是用 rsync 同步通用一些。
主要是自己的 WD MyCloud Gen1 在编译软件的时候,依赖 Wheezy ,Jessie 版本的软件包,又没办法升级系统,只能是自己建立软件源,保存一下,免得日后麻烦。
由于 Debian 源的结构,要单独分版本来同步很不方便,包都集中在 /pool 目录下,故此脚本主要根据索引文件来生成该版本的包列表ARCH_EXCLUDE 用来过滤不同架构的包的dists 用来过滤不同版本的同步完成后,整个 Wheezy/Jessie 源(i386, amd64, arm, source) 共 96G
Wheezy Archive 源设置
|
1 2 |
deb http://mirrors.163.com/debian-archive/ wheezy main contrib non-free deb-src http://mirrors.163.com/debian-archive/ wheezy main contrib non-free |
同步脚本代码
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 |
#!/bin/sh #author: igi #date: 2012-03-28 NAME="debian" SYNC_FILES="$NAME"_files #TO="/tmp/$NAME" TO="./$NAME" FROM="archive.debian.org::debian-archive/debian" #FROM="debian.ethz.ch::debian-archive/debian" #FROM="mirror.1und1.de::debian-archive/debian" #FROM="debian.koyanet.lv::debian-archive/debian" #RUNDIR="/tmp/" RUNDIR="./" ARCH_EXCLUDE="alpha hppa hurd-i386 ia64 kfreebsd-amd64 kfreebsd-i386 mips mipsel powerpc s390 s390x sparc ppc64el" for ARCH in $ARCH_EXCLUDE; do EXCLUDE=$EXCLUDE"\ --exclude binary-$ARCH/ \ --exclude *_$ARCH.deb \ --exclude *_$ARCH.udeb \ --exclude installer-$ARCH/ \ --exclude Contents-$ARCH* " done #dists='lenny etch' dists='wheezy jessie' for dist in $dists; do DIST_INCLUDE=${DIST_INCLUDE}"\ --include /dists/$dist/ \ --include /dists/$dist/contrib/ \ --include /dists/$dist/main/ \ --include /dists/$dist/non-free/ " DIST_EXCLUDE="${DIST_EXCLUDE}\ --exclude /dists/$dist/* " done #sync index files rsync --progress -av \ --include 'Packages.gz' \ --include 'Sources.gz' \ $DIST_INCLUDE \ --include '/dists/' \ --exclude '/*' \ --exclude '/dists/*' \ $DIST_EXCLUDE \ --exclude 'i18n' \ --exclude 'installer-amd64' \ --exclude 'installer-i386' \ --exclude 'installer-armel' \ --exclude 'installer-arm64' \ --exclude 'installer-armhf' \ --exclude 'installer-ppc64el' \ --exclude 'Release' \ --exclude '*.bz2' \ $EXCLUDE \ "$FROM/" "$TO/" rm -rf "$RUNDIR"/"$SYNC_FILES" find "$TO/dists/" -name 'Packages.gz' -exec zgrep 'Filename: ' {} + | awk '{print $2}' >"$RUNDIR"/"$SYNC_FILES" find "$TO/dists/" -name 'Sources.gz' -exec zcat {} + | awk '/Package:/{dir="";delete files;next};/Directory:/{dir=$2;next};/Files:/{pass=1;next}; pass && /^ / {files[NR]=$NF}; length(files) && dir && / /{for(i in files) print dir"/"files[i];delete files}; /^[^ ]/{pass=0;next};' >>"$RUNDIR"/"$SYNC_FILES" #first stage rsync --progress -v --recursive --times --links --hard-links \ --files-from="$RUNDIR"/"$SYNC_FILES" \ "$FROM/" "$TO/" #second stage rsync --progress -v --recursive --times --links --hard-links \ $DIST_INCLUDE \ --exclude '/dists/*' \ $EXCLUDE \ --exclude '/pool/' \ "$FROM/" "$TO/" |
更多 debian-archive 源,见: http://www.debian.org/distrib/archive
Debian 系统启动非常耗时,每次启动都要等待1分30秒的任务超时才能启动,屏幕显示“A start job is running for /dev/disk/by-uuid/...a71b-4040-9b53-e92525f6803e”,如下图:Debian 10(代号为Buster)已经正式发布,可以开始尝鲜Debian 10了。 需要逐版本升级,不要跨版本升级,目前的尝试来看,跨版本升级会出现问题。
1. 更新Debian Jessie到最新版
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
$ su $ apt-get update $ apt-get upgrade $ apt-get dist-upgrade |
2. 将软件源改为Stretch安装源
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
$ su $ sed -i 's/jessie/stretch/g' /etc/apt/sources.list # 替换成国内镜像源(清华大学) $ sed -i 's/deb.debian.org/mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/g' /etc/apt/sources.list $ sed -i 's/security.debian.org/mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn\/debian-security/g' /etc/apt/sources.list |
3. 升级系统版本
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
$ su $ apt-get update $ apt-get dist-upgrade |
4. 重启
|
1 2 3 |
$ su $ reboot |
5. 更新Debian Stretch到最新版
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
$ su $ apt-get update $ apt-get upgrade $ apt-get dist-upgrade $ apt-get autoremove |
6. 将软件源改为Buster安装源
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
$ su $ sed -i 's/stretch/buster/g' /etc/apt/sources.list # 替换成国内镜像源(清华大学) $ sed -i 's/deb.debian.org/mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/g' /etc/apt/sources.list $ sed -i 's/security.debian.org/mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn\/debian-security/g' /etc/apt/sources.list |
7. 升级系统版本
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
$ su $ apt-get update $ apt-get dist-upgrade |
8. 重启
|
1 2 3 |
$ su $ reboot |
9. 清理安装包
|
1 |
$ sudo apt-get autoremove |
由Inria Flower实验室(位于法国波尔多)研究小组创建的 Poppy,是一台经济实惠、易于安装的人形机器人,拥有强大而灵活的硬件配置。使用现成部件(电机及电子元件)和 3D打印的肢体,降低创客自制门槛。
上节介绍了如何使用起泡排序的思想对无序表中的记录按照一定的规则进行排序,本节再介绍一种排序算法——快速排序算法(Quick Sort)。
C语言中自带函数库中就有快速排序——qsort函数 ,包含在 <stdlib.h> 头文件中。
快速排序算法是在起泡排序的基础上进行改进的一种算法,其实现的基本思想是:通过一次排序将整个无序表分成相互独立的两部分,其中一部分中的数据都比另一部分中包含的数据的值小,然后继续沿用此方法分别对两部分进行同样的操作,直到每一个小部分不可再分,所得到的整个序列就成为了有序序列。
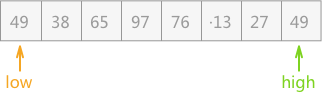
例如,对无序表{49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49}进行快速排序,大致过程为:
{27,38,13,49,65,97,76,49};{27,38,13}和{65,97,76,49},继续采用此种方法分别对两个子表进行排序;{13,27,38},此部分已经有序;后部分子表以 65 为支点,排序后的子表为{49,65,97,76};{49}和{97,76},前者不需排序,后者排序后的结果为{76,97};{13,27,38}、{49}、{49}、{65}、{76,97}构成有序表:{13,27,38,49,49,65,76,97};整个过程中最重要的是实现第 2 步的分割操作,具体实现过程为:



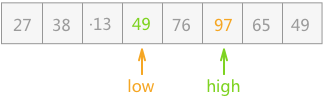
该操作过程的具体实现代码为:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
#define MAX 8 typedef struct { int key; }SqNote; typedef struct { SqNote r[MAX]; int length; }SqList; //交换两个记录的位置 void swap(SqNote *a,SqNote *b){ int key=a->key; a->key=b->key; b->key=key; } //快速排序,分割的过程 int Partition(SqList *L,int low,int high){ int pivotkey=L->r[low].key; //直到两指针相遇,程序结束 while (low<high) { //high指针左移,直至遇到比pivotkey值小的记录,指针停止移动 while (low<high && L->r[high].key>=pivotkey) { high--; } //交换两指针指向的记录 swap(&(L->r[low]), &(L->r[high])); //low 指针右移,直至遇到比pivotkey值大的记录,指针停止移动 while (low<high && L->r[low].key<=pivotkey) { low++; } //交换两指针指向的记录 swap(&(L->r[low]), &(L->r[high])); } return low; } |
该方法其实还有可以改进的地方:在上边实现分割的过程中,每次交换都将支点记录的值进行移动,而实际上只需在整个过程结束后(low==high),两指针指向的位置就是支点记录的准确位置,所以无需每次都移动支点的位置,最后移动至正确的位置即可。
所以上边的算法还可以改写为:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
//此方法中,存储记录的数组中,下标为 0 的位置时空着的,不放任何记录,记录从下标为 1 处开始依次存放 int Partition(SqList *L,int low,int high){ L->r[0]=L->r[low]; int pivotkey=L->r[low].key; //直到两指针相遇,程序结束 while (low<high) { //high指针左移,直至遇到比pivotkey值小的记录,指针停止移动 while (low<high && L->r[high].key>=pivotkey) { high--; } //直接将high指向的小于支点的记录移动到low指针的位置。 L->r[low]=L->r[high]; //low 指针右移,直至遇到比pivotkey值大的记录,指针停止移动 while (low<high && L->r[low].key<=pivotkey) { low++; } //直接将low指向的大于支点的记录移动到high指针的位置 L->r[high]=L->r[low]; } //将支点添加到准确的位置 L->r[low]=L->r[0]; return low; } |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 |
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define MAX 9 //单个记录的结构体 typedef struct { int key; }SqNote; //记录表的结构体 typedef struct { SqNote r[MAX]; int length; }SqList; //此方法中,存储记录的数组中,下标为 0 的位置时空着的,不放任何记录,记录从下标为 1 处开始依次存放 int Partition(SqList *L,int low,int high){ L->r[0]=L->r[low]; int pivotkey=L->r[low].key; //直到两指针相遇,程序结束 while (low<high) { //high指针左移,直至遇到比pivotkey值小的记录,指针停止移动 while (low<high && L->r[high].key>=pivotkey) { high--; } //直接将high指向的小于支点的记录移动到low指针的位置。 L->r[low]=L->r[high]; //low 指针右移,直至遇到比pivotkey值大的记录,指针停止移动 while (low<high && L->r[low].key<=pivotkey) { low++; } //直接将low指向的大于支点的记录移动到high指针的位置 L->r[high]=L->r[low]; } //将支点添加到准确的位置 L->r[low]=L->r[0]; return low; } void QSort(SqList *L,int low,int high){ if (low<high) { //找到支点的位置 int pivotloc=Partition(L, low, high); //对支点左侧的子表进行排序 QSort(L, low, pivotloc-1); //对支点右侧的子表进行排序 QSort(L, pivotloc+1, high); } } void QuickSort(SqList *L){ QSort(L, 1,L->length); } int main() { SqList * L=(SqList*)malloc(sizeof(SqList)); L->length=8; L->r[1].key=49; L->r[2].key=38; L->r[3].key=65; L->r[4].key=97; L->r[5].key=76; L->r[6].key=13; L->r[7].key=27; L->r[8].key=49; QuickSort(L); for (int i=1; i<=L->length; i++) { printf("%d ",L->r[i].key); } return 0; } |
运行结果:
|
1 |
13 27 38 49 49 65 76 97 |
快速排序算法的时间复杂度为O(nlogn),是所有时间复杂度相同的排序方法中性能最好的排序算法。
I2C 总线在物理连接上非常简单,分别由SDA(串行数据线)和SCL(串行时钟线)及上拉电阻组成。通信原理是通过对SCL和SDA线高低电平时序的控制,来产生I2C总线协议所需要的信号进行数据的传递。在总线空闲状态时,这两根线一般被上面所接的上拉电阻拉高,保持着高电平。
I2C通信方式为半双工,只有一根SDA线,同一时间只可以单向通信,RS485也为半双工,SPI和UART为双工。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
$ sudo apt-get install samba $ sudo apt-get install system-config-samba $ sudo apt-get install libcanberra-gtk-module $ sudo touch /etc/libuser.conf $ sudo system-config-samba |