git-flow 的工作流程
当在团队开发中使用版本控制系统时,商定一个统一的工作流程是至关重要的。Git 的确可以在各个方面做很多事情,然而,如果在你的团队中还没有能形成一个特定有效的工作流程,那么混乱就将是不可避免的。
基本上你可以定义一个完全适合你自己项目的工作流程,或者使用一个别人定义好的。
在这章节中我们将一起学习一个当前非常流行的工作流程 git-flow。
什么是 git-flow?
一旦安装安装 git-flow,你将会拥有一些扩展命令。这些命令会在一个预定义的顺序下自动执行多个操作。是的,这就是我们的工作流程!
git-flow 并不是要替代 Git,它仅仅是非常聪明有效地把标准的 Git 命令用脚本组合了起来。
严格来讲,你并不需要安装什么特别的东西就可以使用 git-flow 工作流程。你只需要了解,哪些工作流程是由哪些单独的任务所组成的,并且附带上正确的参数,以及在一个正确的顺序下简单执行那些对应的 Git 命令就可以了。当然,如果你使用 git-flow 脚本就会更加方便了,你就不需要把这些命令和顺序都记在脑子里。
安装 git-flow
最新的git bash已经支持,不用安装,或者使用 Sourcetree。
要了解安装 git-flow 细节,请阅读下面这个文档 official documentation。
在项目中设置 git-flow
当你想把你的项目 “切换” 到 git-flow 上后,Git 还是可以像往常一样工作的。这完全是取决于你在仓库上使用特殊的 git-flow 命令或是普通的 Git 命令。换句话说,git-flow 它不会以任何一种戏剧性的方式来改变你的仓库。
话虽如此,git-flow 却存在一些限制。让我们开始在一个新的项目上初始化它吧,之后我们就会有所发现:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
$ git flow init Initialized empty Git repository in /Users/tobi/acme-website/.git/ Branch name for production releases: [master] Branch name for "next release" development: [develop] How to name your supporting branch prefixes? Feature branches? [feature/] Release branches? [release/] Hotfix branches? [hotfix/] |
当在项目的根目录执行 “git flow init” 命令时(它是否已经包括了一个 Git 仓库并不重要),一个交互式安装助手将引导您完成这个初始化操作。听起来是不是有点炫,但实际上它只是在你的分支上配置了一些命名规则。
尽管如此,这个安装助手还是允许你使用自己喜欢的名字。我强烈建议你使用默认的命名机制,并且一步一步地确定下去。
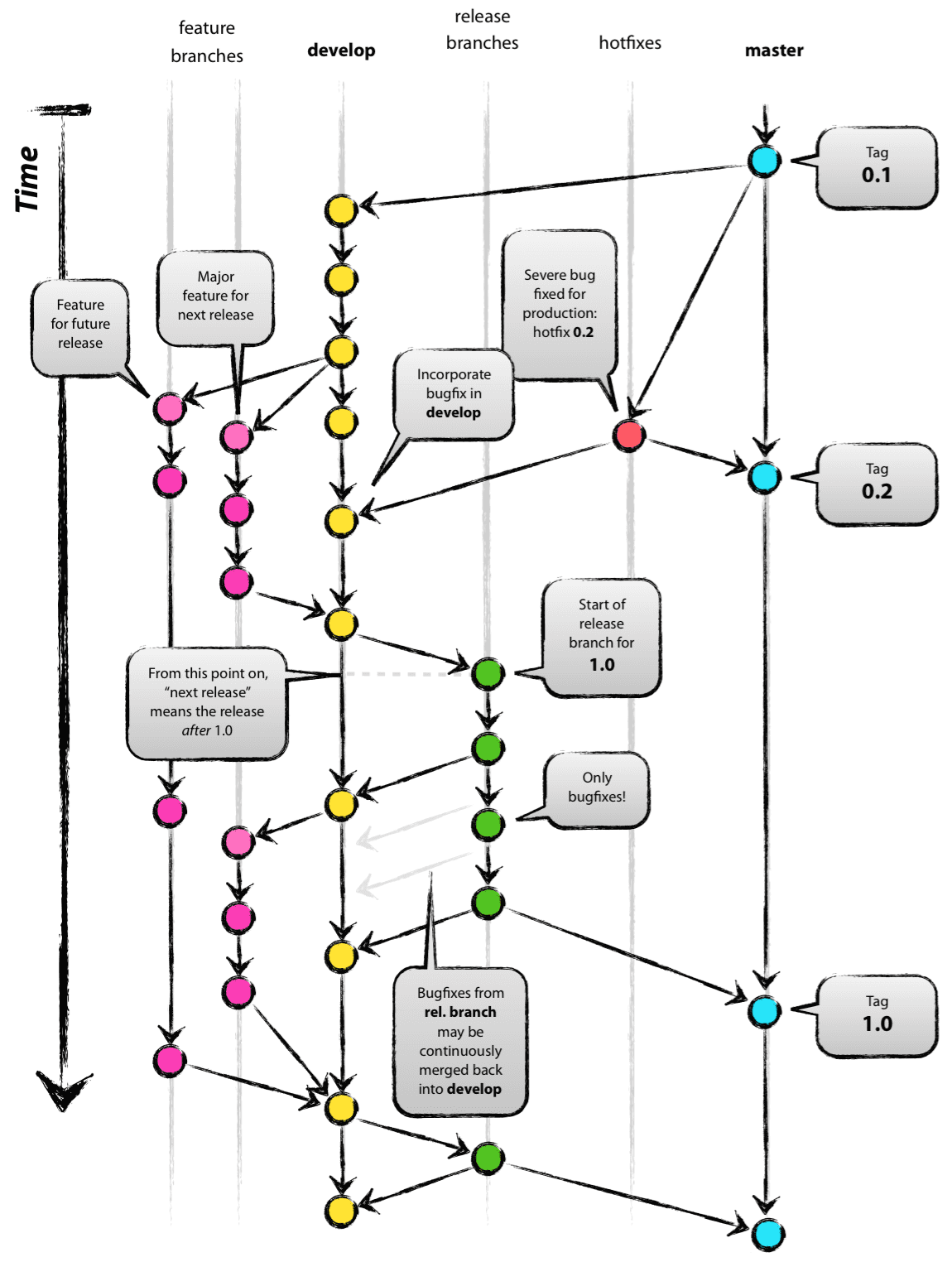
分支的模式
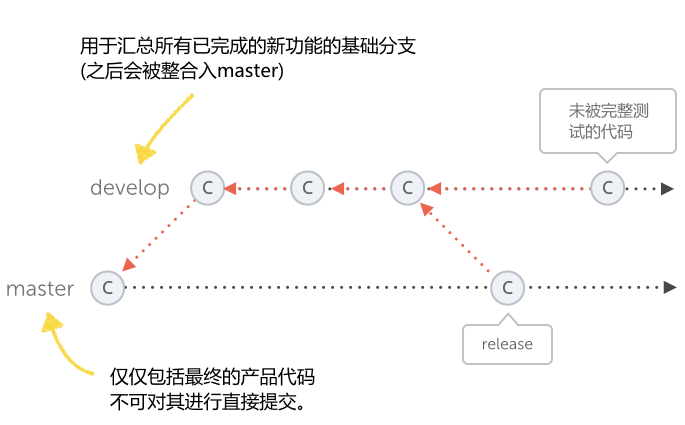
git-flow 模式会预设两个主分支在仓库中:
- master 只能用来包括产品代码。你不能直接工作在这个 master 分支上,而是在其他指定的,独立的特性分支中(这方面我们会马上谈到)。不直接提交改动到 master 分支上也是很多工作流程的一个共同的规则。
- develop 是你进行任何新的开发的基础分支。当你开始一个新的功能分支时,它将是_开发_的基础。另外,该分支也汇集所有已经完成的功能,并等待被整合到 master 分支中。
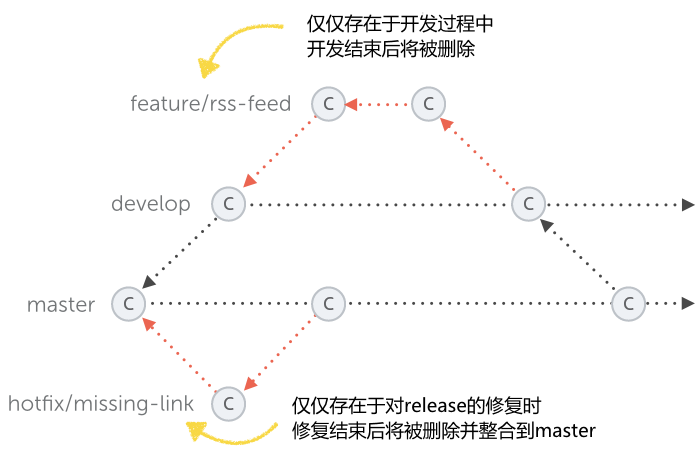
这两个分支被称作为 长期分支。它们会存活在项目的整个生命周期中。而其他的分支,例如针对功能的分支,针对发行的分支,仅仅只是临时存在的。它们是根据需要来创建的,当它们完成了自己的任务之后就会被删除掉。
让我们开始探索一些在现实应用中可能遇到的案例吧!
功能开发
对于一个开发人员来说,最平常的工作可能就是功能的开发。这就是为什么 git-flow 定义了很多对于功能开发的工作流程,从而来帮助你有组织地完成它。
开始新功能
让我们开始开发一个新功能 “rss-feed”:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
$ git flow feature start rss-feed Switched to a new branch 'feature/rss-feed' Summary of actions: - A new branch 'feature/rss-feed' was created, based on 'develop' - You are now on branch 'feature/rss-feed' |
概念
在这些命令的输出文本中,git-flow 会对刚刚完成的操作打印出一个很有帮助的概述
当你需要帮助的时候,你可以随时请求帮助。例如:
正如上面这个新功能一样,git-flow 会创建一个名为 “feature/rss-feed” 的分支(这个 “feature/” 前缀 是一个可配置的选项设置)。你已经知道了,在你做新功能开发时使用一个独立的分支是版本控制中最重要的规则之一。
git-flow 也会直接签出这个新的分支,这样你就可以直接进行工作了。
完成一个功能
经过一段时间艰苦地工作和一系列的聪明提交,我们的新功能终于完成了:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
$ git flow feature finish rss-feed Switched to branch 'develop' Updating 6bcf266..41748ad Fast-forward feed.xml | 0 1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-) create mode 100644 feed.xml Deleted branch feature/rss-feed (was 41748ad). |
最重要的是,这个 “feature finish” 命令会把我们的工作整合到主 “develop” 分支中去。在这里它需要等待:
- 一个在更广泛的 “开发” 背景下的全面测试。
- 稍后和所有积攒在 “develop” 分支中的其它功能一起进行发布。
之后,git-flow 也会进行清理操作。它会删除这个当下已经完成的功能分支,并且换到 “develop” 分支。
管理 releases
Release 管理是版本控制处理中的另外一个非常重要的话题。让我们来看看如何利用 git-flow 创建和发布 release。
创建 release
当你认为现在在 “develop” 分支的代码已经是一个成熟的 release 版本时,这意味着:第一,它包括所有新的功能和必要的修复;第二,它已经被彻底的测试过了。如果上述两点都满足,那就是时候开始生成一个新的 release 了:
|
1 2 |
$ git flow release start 1.1.5 Switched to a new branch 'release/1.1.5' |
请注意,release 分支是使用版本号命名的。这是一个明智的选择,这个命名方案还有一个很好的附带功能,那就是当我们完成了release 后,git-flow 会适当地自动去标记那些 release 提交。
有了一个 release 分支,再完成针对 release 版本号的最后准备工作(如果项目里的某些文件需要记录版本号),并且进行最后的编辑。
完成 release
现在是时候按下那个危险的红色按钮来完成我们的release了:
|
1 |
git flow release finish 1.1.5 |
这个命令会完成如下一系列的操作:
- 首先,git-flow 会拉取远程仓库,以确保目前是最新的版本。
- 然后,release 的内容会被合并到 “master” 和 “develop” 两个分支中去,这样不仅产品代码为最新的版本,而且新的功能分支也将基于最新代码。
- 为便于识别和做历史参考,release 提交会被标记上这个 release 的名字(在我们的例子里是 “1.1.5”)。
- 清理操作,版本分支会被删除,并且回到 “develop”。
从 Git 的角度来看,release 版本现在已经完成。依据你的设置,对 “master” 的提交可能已经触发了你所定义的部署流程,或者你可以通过手动部署,来让你的软件产品进入你的用户手中。
hotfix
很多时候,仅仅在几个小时或几天之后,当对 release 版本作做全面测试时,可能就会发现一些小错误。
在这种情况下,git-flow 提供一个特定的 “hotfix” 工作流程(因为在这里不管使用 “功能” 分支流程,还是 “release” 分支流程都是不恰当的)。
创建 Hotfixes
|
1 |
$ git flow hotfix start missing-link |
这个命令会创建一个名为 “hotfix/missing-link” 的分支。因为这是对产品代码进行修复,所以这个 hotfix 分支是基于 “master” 分支。
这也是和 release 分支最明显的区别,release 分支都是基于 “develop” 分支的。因为你不应该在一个还不完全稳定的开发分支上对产品代码进行地修复。
就像 release 一样,修复这个错误当然也会直接影响到项目的版本号!
完成 Hotfixes
在把我们的修复提交到 hotfix 分支之后,就该去完成它了:
|
1 |
$ git flow hotfix finish missing-link |
这个过程非常类似于发布一个 release 版本:
- 完成的改动会被合并到 “master” 中,同样也会合并到 “develop” 分支中,这样就可以确保这个错误不会再次出现在下一个 release 中。
- 这个 hotfix 程序将被标记起来以便于参考。
- 这个 hotfix 分支将被删除,然后切换到 “develop” 分支上去。
还是和产生 release 的流程一样,现在需要编译和部署你的产品(如果这些操作不是自动被触发的话)。
回顾一下
最后,在结束这个章节之前,我要再次强调几个重点。
首先,git-flow 并不会为 Git 扩展任何新的功能,它仅仅使用了脚本来捆绑了一系列 Git 命令来完成一些特定的工作流程。
其次,定义一个固定的工作流程会使得团队协作更加简单容易。无论是一个 “版本控制的新手” 还是 “Git 专家”,每一个人都知道如何来正确地完成某个任务。
记住,使用 git-flow 并不是必须的。当积攒了一定的使用经验后,很多团队会不再需要它了。当你能正确地理解工作流程的基本组成部分和目标的之后,你完全可以定义一个属于你自己的工作流程。
上面的工作流程不涉及到代码评审过程,开发人员开发完就可以合并分支。但是如果合并分支之前需要进行代码评审,那么整个流程就变复杂,我们下面分析增加了代码评审情况下的工作流。
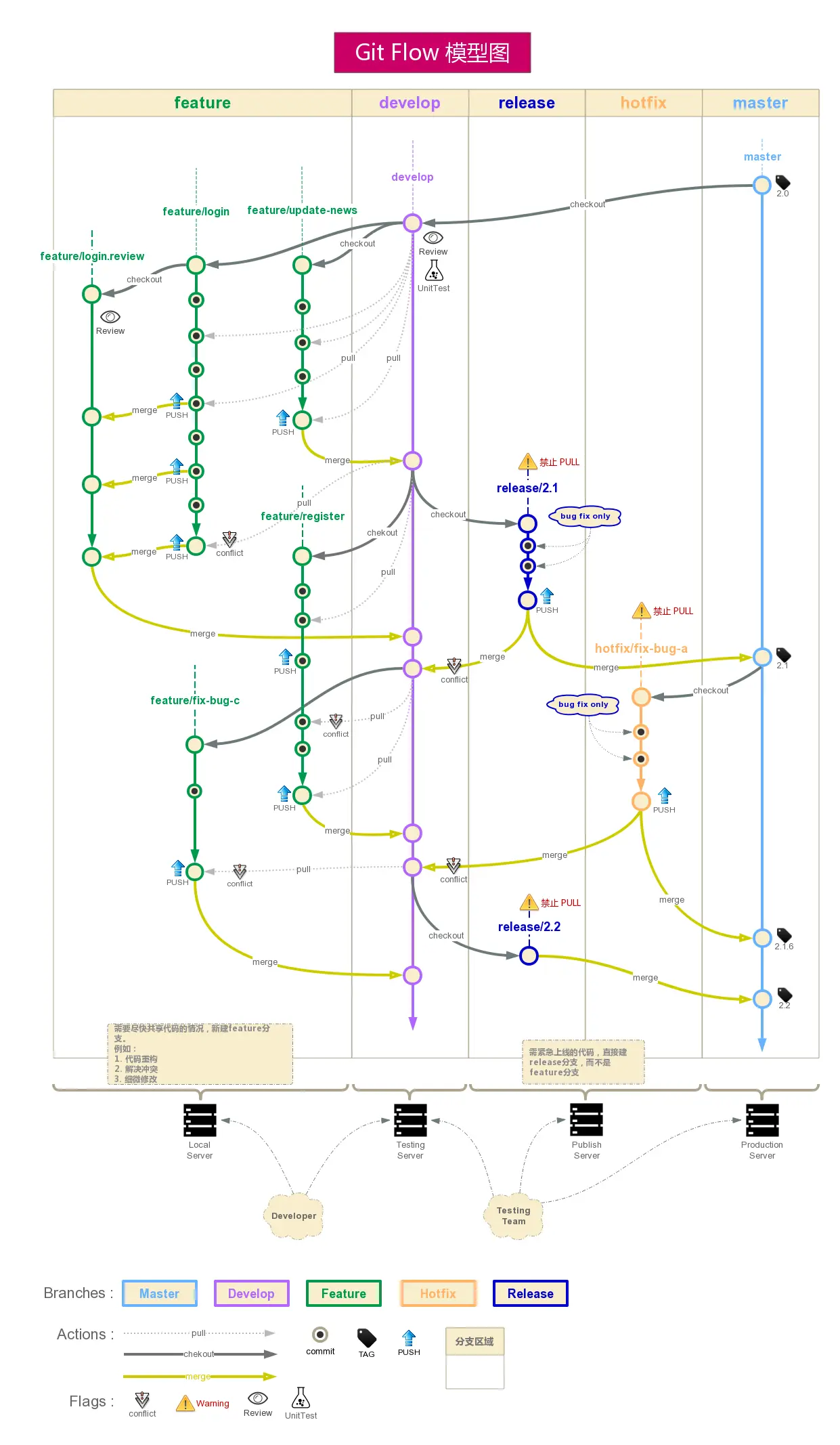
代码评审下的 git-flow 的工作流程
我们使用 Git Flow 来进行版本管理控制,它相对于 GitHub Flow 更适合在产品开发中快速迭代,这种代码管理模式应该已经广泛使用了。
另外,我们鼓励使用 Git 客户端 SourceTree,它集成了 Git Flow 的一些基本操作。如果严格遵循 Git Flow 的流程进行版本管理控制,那么我们只用管开始和结束一个 Feature/Release/Hotfix,基本上是不用手动 merge 分支的。
新功能开发流程
- 从 develop 分支创建 feature 分支;
- 开发调试完将 feature 分支提交到远程版本库;
- 提交 pull request 请求合并到 develop 分支;
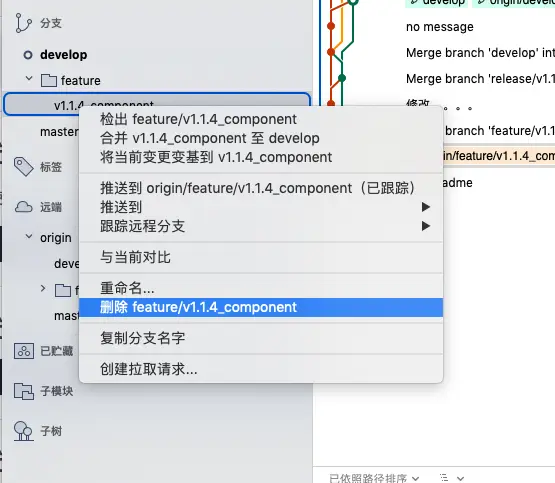
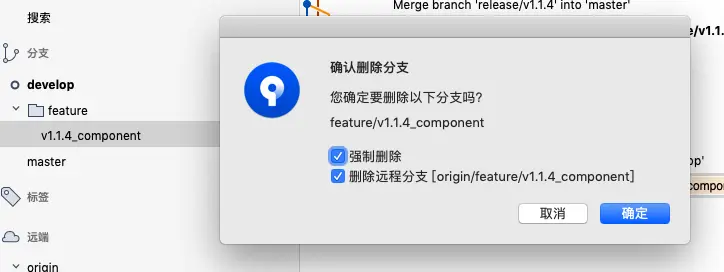
- 相关负责人 code review 后如果同意合并后,删除远程 feature 分支,如果不同意,重新修改后再上传 feature 分支请求 pull request。
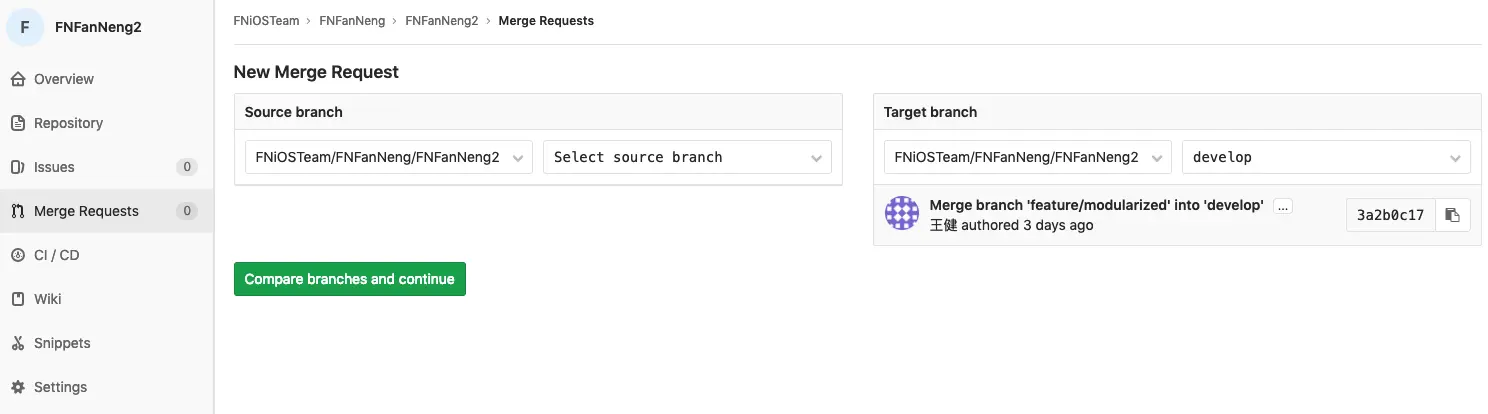
Pull Request
Pull Request是当功能开发者完成一个新功能后向项目维护者发送合并请求通知的机制。它的使用过程如下:
功能开发者可以通过Gitlab页面发送pull request开发管理员自己或组织其他的团队成员审查、讨论和修改代码开发管理员合并新增功能分支到develop分支,然后关闭pull request,并且可以选择删除新增分支
工作流程
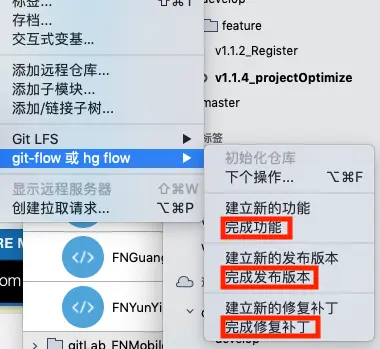
1. 由开发管理员负责在Gitlab上创建空白的仓库,并clone到本地,在sourcetree的git flow菜单中选择初始化仓库,并push到远端。
2. 在Gitlab上设置保护分支,把master、develop分支保护起来,只有指定人可push。
3. 功能开发者clone代码到本地,先在sourcetree的git flow菜单中选择初始化仓库。
4. 然后再开始新建功能分支,进行开发工作。
5. 新功能开发全部完成或部分完成后,功能开发者把最新代码push到远端同样的新功能分支里,并在Gitflow发起pull request给开发管理员
6. 开发管理员review代码,选择合并代码到develop,并可选择删除已经合并的新功能分支
7. 当开发管理员处理完合并请求后,开发者,切换到develop分支,直接删除自己的本地分支及远程分支,不要点击完成(Finish Feature),此时开发者pull远端develop分支最新代码即可,可忽视本地的push提醒。
8. release、hotfix分支和feature分支操作类似。
9. 不可点击完成新功能、完成发布版本、完成修复补丁,因为这样会导致自动合并代码到master或develop分支
Git Flow Release
到此为止,我们发现整个的工作流还算可以接受,但是执行 git flow release 的时候,会发现由于 Git Flow 总是假定我们合并的分支可以立即部署到生产环境,所以如果我们的工作流程符合这个过程,是很简单的。
但是更多的时候,我们会遇到同时开发可功能模块A、B、C,最终上线只上线A、C的情况,这种情况下,会涉及到版本会退的问题,这个时候 git flow 反倒是不方便使用了。
这种情况下,GitLab Flow 流程可能更适合我们的工作流程。
参考链接
- git-flow 的工作流程
- Git Flow详细介绍和使用
- 如何看待 Git flow 发明人称其不适用于持续交付?
- 真正的敏捷工作流 —— GitHub flow
- 一文弄懂 Gitflow、Github flow、Gitlab flow 的工作流
- 别再推荐 Git Flow 了
- A successful Git branching model
- 这才是真正的 Git——分支合并
- GitFlow+Gitlab工作流及Git规范
- git 在命令行提交merge request
- git-flow
- 一个可以提高开发效率的命令:cherry-pick
- Git cherry-pick 这个命令你会经常用到!
- Git Flow与Gitlab Flow两种工作流中,release分支的不同作用
- [译] GitLab Flow简介
- 一文弄懂 Gitflow、Github flow、Gitlab flow 的工作流
- 基于 Git 的分支策略,你值得一看!
- Git分支管理最佳实践