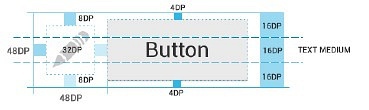
Android4.0设计规定的有效可触摸的UI元素标准是48dp,转化为一个物理尺寸约为9毫米。7~10毫米,这是一个用户手指能准确并且舒适触摸的区域。
如下图所示,你的UI元素可能小于48dp,图标仅有32dp,按钮仅有40dp,但是他们的实际可操作焦点区域最好都应达到48dp的大小。
为使小的UI区域获得良好的触摸交互,根据View的特性,目前碰到了两种情况:
1.如ImageView,设置其padding值,可触摸区域将向外扩展;
2.如Button,设置其padding值,可触摸区域不变,其内内容显示区域向内压缩;
情况1的控件,可直接设置其padding值达到目的,如 android:padding="10dp"
情况2的控件,可使用TouchDelegate动态修改其触摸区域,达到扩大点击范围的效果
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 |
/** * 扩大View的触摸和点击响应范围,最大不超过其父View范围 * * @param view * @param top * @param bottom * @param left * @param right */ public static void expandViewTouchDelegate(final View view, final int top, final int bottom, final int left, final int right) { ((View) view.getParent()).post(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Rect bounds = new Rect(); view.setEnabled(true); view.getHitRect(bounds); bounds.top -= top; bounds.bottom += bottom; bounds.left -= left; bounds.right += right; TouchDelegate touchDelegate = new TouchDelegate(bounds, view); if (View.class.isInstance(view.getParent())) { ((View) view.getParent()).setTouchDelegate(touchDelegate); } } }); } |
采取此种方法的两点注意:
1、若View的自定义触摸范围超出Parent的大小,则超出的那部分无效。
2、一个Parent只能设置一个View的TouchDelegate,设置多个时只有最后设置的生效。
若需要恢复该View的触摸范围:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
/** * 还原View的触摸和点击响应范围,最小不小于View自身范围 * * @param view */ public static void restoreViewTouchDelegate(final View view) { ((View) view.getParent()).post(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Rect bounds = new Rect(); bounds.setEmpty(); TouchDelegate touchDelegate = new TouchDelegate(bounds, view); if (View.class.isInstance(view.getParent())) { ((View) view.getParent()).setTouchDelegate(touchDelegate); } } }); } |
使用TouchDelegate扩大View的触摸响应范围是一种比较灵活的方法,有时可与设置padding的方式结合使用。
更新
======
后期实际开发中发现,使用post runnable的方式去设置Delegate区域大小的原因是,如该View师在Activity的OnCreate()或Fragment的OnCreateView()中绘制,此时UI界面尚未开始绘制,无法获得正确的坐标;
若将此法应用在ListView的getView()中绘制每个ItemView时,则Delegate的设置将部分失效,原因是ListView的绘制较特殊,可能无法获取到部分还未绘制出的View的正确坐标。解决方案具体可参考以下参考阅读所列。
参考阅读:通过自定义View的方式,及某些其他情况的处理:
1.《Android使用TouchDelegate增加View的触摸范围》 http://blog.csdn.net/sgwhp/article/details/10963383
2.《ListView Tips & Tricks #5: Enlarged Touchable Areas》 http://cyrilmottier.com/2012/02/16/listview-tips-tricks-5-enlarged-touchable-areas/
3.《Extend touchable areas #Android》 https://plus.google.com/u/0/+JulienDodokal/posts/8zoV3RQvReS